What Does a Pollotarian Eat?
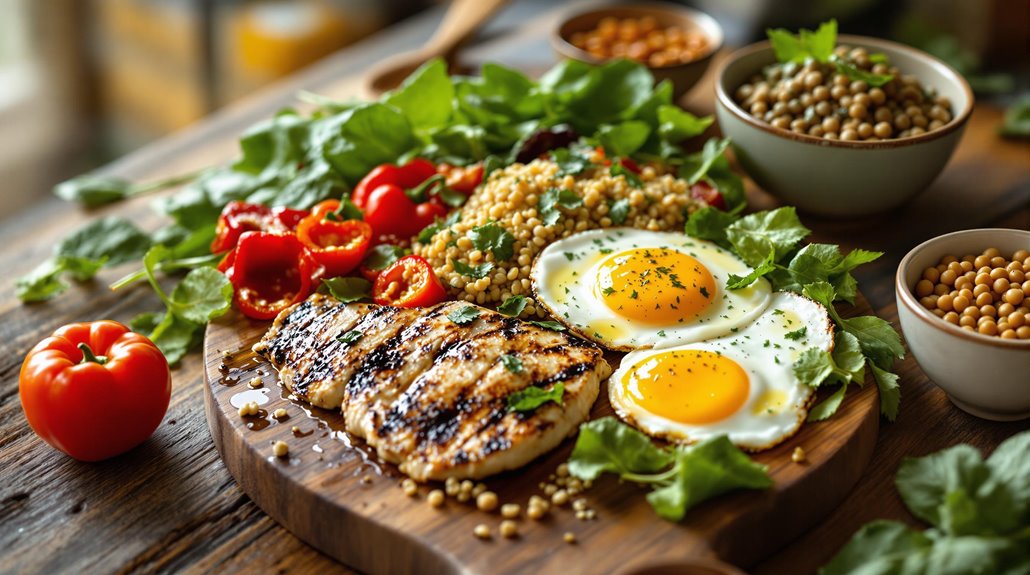

As a pollotarian, you'll eat poultry like chicken, turkey, and duck while avoiding red meat, pork, and fish. Your diet will include plenty of plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. You can also choose to include eggs and dairy products. This flexible eating style supports heart health, weight management, and overall wellness. Uncover how this balanced approach fits perfectly with your health and lifestyle goals.
Understanding the Pollotarian Lifestyle
Ever wondered about a diet that bridges the gap between vegetarianism and meat-eating? The pollotarian lifestyle might be your answer. This unique Diet focuses on eliminating red meat while allowing poultry like Chicken and turkey as protein sources.
As a pollotarian, you'll make conscious choices about which animal products to include in your meals. While some pollotarians choose to consume eggs and dairy products, others opt to exclude them. The flexibility of this eating pattern lets you customize it to your preferences while enjoying significant Health benefits.
You'll find yourself embracing more plant-based foods while still enjoying poultry dishes. This balanced approach helps reduce your environmental impact and potentially lowers your risk of certain diseases associated with red meat consumption. It's a practical middle ground for those seeking a more mindful way of eating. Many pollotarians enhance their protein intake by incorporating high-protein smoothies into their daily routine.
Essential Foods in a Pollotarian Diet
When following a pollotarian diet, you'll build your meals around several essential food groups. This vegetarian-like approach lets you eat chicken and other poultry while increasing your intake of plant-based foods. The combination supports your physical and mental well-being as you eat less red meat.
Your pollotarian meal plan should prioritize these key foods:
- Lean poultry options like chicken, turkey, and duck prepared without heavy processing
- Plant proteins including legumes, nuts, and seeds combined with whole grains
- Fresh fruits and vegetables in abundant quantities for essential nutrients
- Optional dairy products and eggs for additional protein and calcium
Adding antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables to your meals provides vital nutrients while enhancing overall cellular health.
Benefits of Choosing Pollotarian Eating

Why are more people switching to pollotarian eating? The health benefits are persuasive, especially when you eat less red meat. By choosing to eat chicken and other poultry instead of eating red meat, you'll drastically lower your risk of heart disease and certain cancers.
A pollotarian diet can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce the likelihood of obesity. If you're concerned about type 2 diabetes, this eating style may help manage the condition and decrease mortality risks.
While some pollotarians include fish in their diet, the focus remains on poultry and plant-based foods, offering many of the same benefits as vegetarian diets. Making nutritious smoothies with fibrous fruits and vegetables can be an excellent way to supplement a pollotarian diet with essential nutrients.
Creating a Balanced Pollotarian Meal Plan
Creating a balanced pollotarian meal plan requires thoughtful planning to confirm you're getting all essential nutrients. By replacing red meat with poultry, you'll need to focus on incorporating diverse protein sources, including eggs and dairy, duck and turkey, and plant-based options.
While animal products like granary bread can provide vitamin B, you'll want to structure your meals thoughtfully throughout the day.
- Start with protein-rich breakfasts featuring eggs or Greek yogurt
- Pack lunches with lean chicken on granary bread and plenty of vegetables
- Plan dinners around turkey or duck with whole grains and leafy greens
- Include nutrient-dense snacks like nuts, seeds, and fruits between meals
This approach establishes you're meeting your nutritional needs while maintaining a satisfying pollotarian lifestyle.
Common Nutritional Considerations

While following a balanced meal plan is important, understanding specific nutritional considerations can help you thrive on a pollotarian diet. By replacing red meat with poultry, you'll naturally consume less saturated fat while still getting essential protein and B vitamins.
However, following a pollotarian diet requires careful attention to certain nutrients typically found in red meat and other animal products.
Since your diet is primarily plant-based with the inclusion of poultry, you'll need to monitor your intake of iron, zinc, vitamin B12, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids to prevent nutritional deficiencies. You can meet these needs by eating a diverse range of plant foods like legumes, whole grains, nuts, and seeds. Consider taking supplements, especially vitamin B12, if blood tests indicate you're not getting enough through your diet alone.
Tips for Transitioning to Pollotarian Eating
Making the switch to a pollotarian diet becomes easier when you take a gradual, strategic approach. For several reasons, starting your transition by slowly replacing red meat with moderate amounts of poultry means chicken and other birds will become your primary protein source. You're less likely to feel overwhelmed when you make incremental changes, and this approach can even help you identify new favorite dishes.
Start experimenting with different poultry options like turkey, duck, and game birds. Source high-quality birds from local farms to verify ethical practices. Stock your kitchen with whole grains and fresh produce. Incorporate plant-based proteins to confirm your diet is low in nutritional gaps.
This balanced approach reduces your increased risk of dietary deficiencies while making the transition more sustainable and enjoyable.
Environmental Impact of the Pollotarian Diet

The environmental footprint of a pollotarian diet offers three distinct advantages over traditional meat-heavy diets. When you choose to be someone who eats a semi-vegetarian diet focused on forms of poultry, you'll considerably reduce your environmental impact compared to consuming red meat. This diet requires less land and water usage while producing fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
Though not as environmentally friendly as a vegetarian or vegan diet, the pollotarian approach represents a practical step towards sustainability. By combining poultry with plenty of plant-based foods, you'll maintain a high-protein diet while lowering your saturated fat intake and environmental footprint. The emphasis on fruits, vegetables, and grains, combined with moderate poultry consumption, helps mitigate the environmental toll of livestock production while still providing satisfying meal options.